Platform-Tools 命令行工具
Android SDK Platform-Tools 是 Android SDK 的一个组件。它包含与 Android 平台进行交互的工具。
TIP
adb 与 fastboot 组件包含在 Platform-Tools 内。
- 官方 ADB 资料
- 官方 ADB 资料 新版,暂无中文
- 官网下载(Platform-Tools 内包含 ADB 等所有工具)
- 封装版本:Android_SDK_Platform_Tools_v33.0.0.exe - 123 云盘 本站封装
- 基础知识 > 危险权限 > ADB 介绍 - 刷机指南
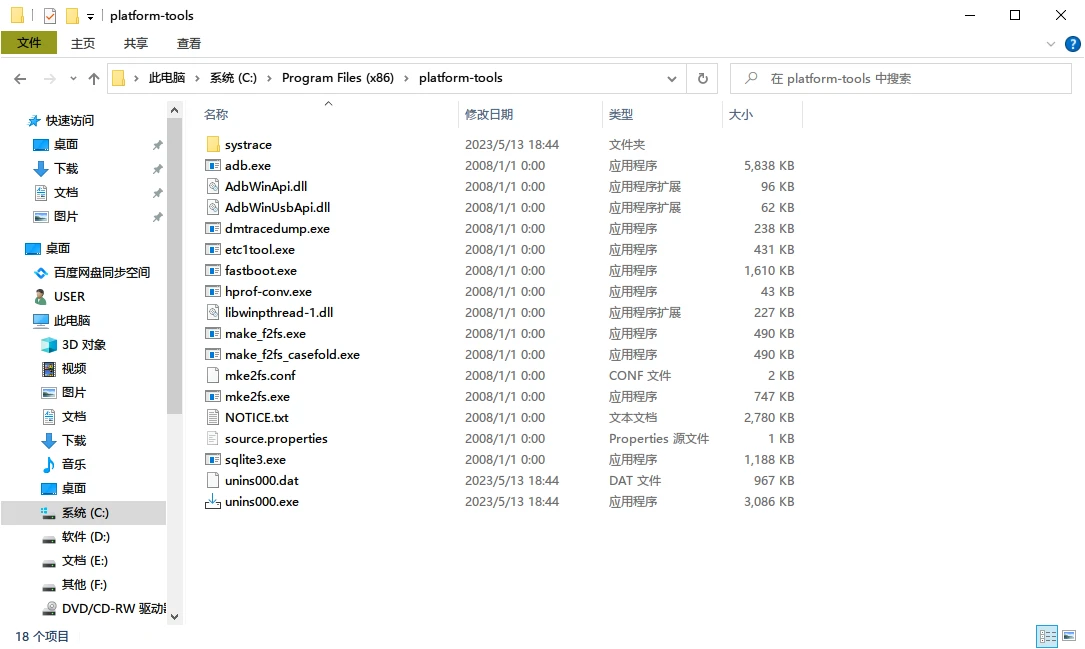
Platform-Tools 下载与安装
TIP
Android Studio 会自动下载 Platform-Tools。如果您曾今使用过 Android Studio,则可能无需手动下载此工具,直接配置环境变量即可。
(如果您不知道 Android Studio 是什么,则说明此消息对您无用,您需要继续阅读下面的内容)
部分工具、工具箱、手机助手内自带 ADB 组件,而 Platform-Tools 内其他组件很少用得到,因此大部分情况下您无需手动安装 Platform-Tools。
您可以选择一键安装方法,或者是原始安装方法。
对于一般人来说,推荐一键安装,安装器会自动帮助用户配置一系列设置的。
一键安装 对小白友好
Windows 一键安装
您可以下载第三方封装好的版本,傻瓜式安装,推荐小白使用:
- Android_SDK_Platform_Tools_v33.0.0.exe - 123 云盘 本站封装
本站封装的版本可以直接在控制面板中卸载,卸载后会自动移除环境变量
WARNING
通过傻瓜式安装的 Platform-Tools 版本可能低于官网版本,小部分功能可能无法使用。
TIP
一般人的电脑装的都是 Windows,因此看本段教程安装就可以了。
Linux 一键安装
您可以使用 apt 等包管理器一键安装
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt install android-sdk-platform-toolssudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt install android-sdk-platform-tools2
3
TIP
使用包管理工具安装的 Platform-tools 不包含 adb,您可能需要手动安装 adb。
sudo apt install adbsudo apt install adbAndroid 一键安装
没错,安卓也可以用此工具。借助此特性,您甚至可以拿一台安卓手机给另一台安卓手机解锁、刷机。
- Magisk 模块:提供 Magisk 安装的 ADB 或者其他工具在整个操作系统内是共享的,您可以在几乎任何地方使用。
- 第三方工具:第三方工具通常提供内置的 ADB 组件。部分工具也提供写入到系统的功能,但是这可能破坏系统,建议使用 Magisk 模块代替。
- Termux、MT 管理器:与 Linux 相同,但是您也可以使用 Termux 专属的
pkg来安装 ADB。
原始方法安装
首先进入官网下载 Platform-Tools 压缩包(Platform-Tools 内包含 ADB)
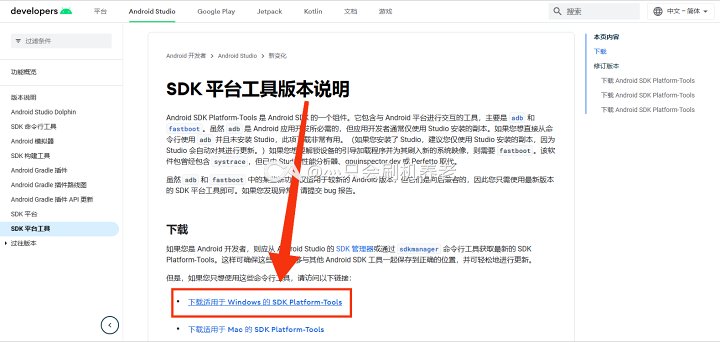
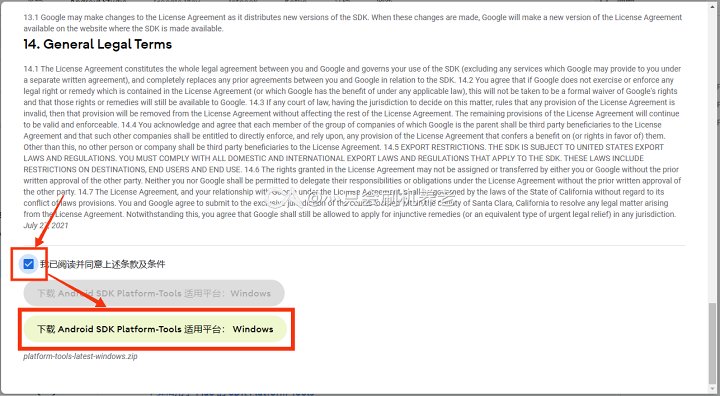
TIP
官方 Platform-Tools 是绿色版本,您可以将下载的压缩包解压到任何地方,但是一定不要删除这些文件!
下载完成之后,您可以按照这篇文章配置环境变量:《Win11配置ADB环境变量教程》
TIP
如果您只是临时使用,您可以直接在地址栏中输入
cmd,在 Platform-Tools 所在目录下启动命令提示符,直接使用相关软件(如adb.exe)。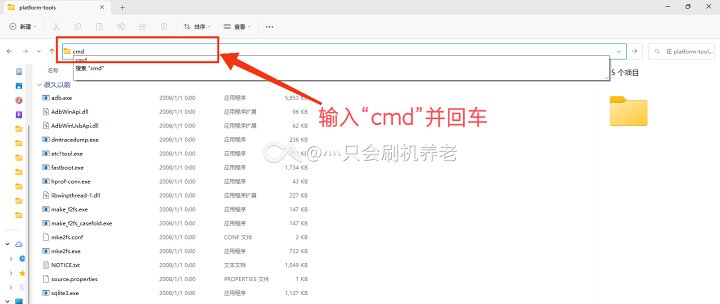
TIP
配置好 ADB 后,您可能还需要安装或修复驱动
检测工具是否被正常安装
- 打开终端,在 Windows 中为
Windows 终端、终端、命令提示符(也叫 cmd) - 运行命令
adb version,如果弹出了版本信息,则说明安装成功
C:\Users\USER>adb version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 33.0.0-8141338
Installed as C:\Program Files (x86)\platform-tools\adb.exeC:\Users\USER>adb version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 33.0.0-8141338
Installed as C:\Program Files (x86)\platform-tools\adb.exePS C:\Users\USER> adb version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 33.0.0-8141338
Installed as C:\Program Files (x86)\platform-tools\adb.exePS C:\Users\USER> adb version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 33.0.0-8141338
Installed as C:\Program Files (x86)\platform-tools\adb.exeuser@DESKTOP-93UT1LQ:~$ adb version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 28.0.2-debian
Installed as /usr/lib/android-sdk/platform-tools/adbuser@DESKTOP-93UT1LQ:~$ adb version
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.41
Version 28.0.2-debian
Installed as /usr/lib/android-sdk/platform-tools/adb实际的版本号与示例不匹配没关系,大部分情况不影响使用。
ADB 工具
有关 ADB 工具的更多用法,请参考以下链接:
- 基础知识 > 危险权限 > ADB - 刷机指南
- 官方 ADB 资料 - Android 开发者
- 官方 ADB 资料 新版,暂无中文 - Android 开发者
adb 中文帮助文件
仅供参考
Android Debug Bridge 版本 1.0.31
-a - 指示 adb 监听所有接口上的连接
-d - 将命令指向唯一连接的 USB 设备,如果存在多个 USB 设备,则返回错误信息。
-e - 将命令指向唯一运行的模拟器。
如果运行的模拟器超过一个,则返回错误信息。
-s <特定设备> - 将命令指向具有给定序列号或限定符的设备或模拟器。覆盖 ANDROID_SERIAL 环境变量。
-p <产品名称或路径> - 简单的产品名称,如 "sooner",或产品输出目录的相对/绝对路径,如
"out/target/product/sooner"。 如果未指定 -p,则使用 ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT 环境变量,
该变量必须是绝对路径。
-H - adb 服务器主机名称(默认值:localhost)
-P - adb 服务器的端口(默认值:5037)
devices [-l] - 列出所有已连接的设备 ('-l'也会列出设备限定符)
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP通过 TCP/IP 连接设备
如果没有指定端口号,则默认使用端口 5555。
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - 断开与 TCP/IP 设备的连接。
如果未指定端口号,则默认使用端口 5555。
使用此命令且不带其他参数 将断开与所有已连接 TCP/IP 设备的连接。
设备指令:
adb push <local> <remote> - 将文件/目录复制到设备
adb pull <remote> [<local>] - 从设备复制文件/目录
adb sync [ <目录> ] - 仅在发生变化时复制 主机->设备(-l 表示列出但不复制)(参见 "adb help all")
adb shell - 交互运行远程 shell
adb shell <command> - 运行远程 shell 命令
adb emu <command> - 运行模拟器控制台命令
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - 查看设备日志
adb forward --list - 列出所有前向套接字连接。
格式是一个行列表,格式如下:
<serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
adb forward <local> <remote> - 前向套接字连接
转发规格是
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix 域名套接字名称>
localreserved:<unix 域名套接字名称>
localfilesystem:<unix 域名套接字名称>
dev:<字符设备名>
jdwp:<进程pid> (仅远程)
adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
- 与 "adb forward <local> <remote>" 相同,但如果 <local> 已经转发就会失败
adb forward --remove <local> - 移除特定的转发套接字连接
adb forward --remove-all - 移除所有前向套接字连接
adb jdwp - 列出托管 JDWP 传输的进程的 PID
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <文件>
- 将此软件包文件推送到设备并安装
('-l' 意味着对应用程序进行转发锁定)
('-r' 意味着重新安装应用程序,保留其数据)
('-s' 意味着安装在 SD 卡上,而不是内置存储器上)
('--algo', '--key', 和 '--iv' 表示文件已经加密)
adb uninstall [-k] <包名> - 从设备中删除此应用软件包
('-k' 是指保留数据和缓存目录)
adb bugreport - 返回错误报告中应包含的所有设备信息。
adb backup [-f <文件>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<包名...>]
- 将设备数据存档写入 <文件>。
如果没有提供 -f 选项,数据将写入当前目录下的 "backup.ab"。
(-apk|-noapk 启用/禁用存档中 .apk 本身的备份;默认为 noapk。)
(-obb|-noobb 启用/禁用与每个应用程序相关的任何已安装 apk 扩展(又名 .obb)文件的备份;
默认为 noobb。)
(-shared|-noshared 启用/禁用设备共享存储/SD 卡内容备份;默认为 noshared。)
(-all 表示备份所有已安装的应用程序)
(-system|-nosystem 切 换-all 是否自动包含系统应用程序;默认为包含系统应用程序)
(<包名...> 是要备份的应用程序列表。 如果传递了 -all 或 -shared 标志,
则软件包列表是可选的。 即使 -nosystem 通常会导致省略,
命令行中明确给出的应用程序也会包含在内。)
adb restore <file> - 从 <file> 备份存档恢复设备内容
adb help - 显示此帮助信息
adb version - 显示版本号
脚本:
adb wait-for-device - 阻止,直至设备联机
adb start-server - 确保有服务器在运行
adb kill-server - 如果服务器正在运行,则将其杀死
adb get-state - 打印:offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - 打印:<serial-number>
adb get-devpath - 打印:<device-path>
adb status-window - 连续打印指定设备的设备状态
adb remount - 重新挂载设备上的 /system 分区为读写
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - 重启设备,可选择进入引导加载程序或恢复程序
adb reboot-bootloader - 将设备重启至引导加载程序
adb root - 以 root 权限重启 adbd 守护进程
adb usb - 重启监听 USB 的 adbd 守护进程
adb tcpip <port> - 重启通过 TCP 在指定端口上监听的 adbd 守护进程
网络:
adb ppp <tty> [参数] - 通过 USB 运行 PPP。
注意:不应自动启动 PPP 连接。
<tty> 指 PPP 流的 tty。例如 dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[参数] - 例如 defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb 同步注意事项: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> 可以有多种解释:
- 如果未指定 <directory>,则 /system 和 /data 分区都将被更新。
- 如果是 "system" 或 "data",则只更新相应的分区。
环境变量:
ADB_TRACE - 打印调试信息。以逗号分隔的下列值列表
1 或 all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - 要连接的序列号。如果给定,-s 优先。
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - 与 logcat 选项一起使用时,只打印这些调试标记。Android Debug Bridge 版本 1.0.31
-a - 指示 adb 监听所有接口上的连接
-d - 将命令指向唯一连接的 USB 设备,如果存在多个 USB 设备,则返回错误信息。
-e - 将命令指向唯一运行的模拟器。
如果运行的模拟器超过一个,则返回错误信息。
-s <特定设备> - 将命令指向具有给定序列号或限定符的设备或模拟器。覆盖 ANDROID_SERIAL 环境变量。
-p <产品名称或路径> - 简单的产品名称,如 "sooner",或产品输出目录的相对/绝对路径,如
"out/target/product/sooner"。 如果未指定 -p,则使用 ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT 环境变量,
该变量必须是绝对路径。
-H - adb 服务器主机名称(默认值:localhost)
-P - adb 服务器的端口(默认值:5037)
devices [-l] - 列出所有已连接的设备 ('-l'也会列出设备限定符)
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP通过 TCP/IP 连接设备
如果没有指定端口号,则默认使用端口 5555。
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - 断开与 TCP/IP 设备的连接。
如果未指定端口号,则默认使用端口 5555。
使用此命令且不带其他参数 将断开与所有已连接 TCP/IP 设备的连接。
设备指令:
adb push <local> <remote> - 将文件/目录复制到设备
adb pull <remote> [<local>] - 从设备复制文件/目录
adb sync [ <目录> ] - 仅在发生变化时复制 主机->设备(-l 表示列出但不复制)(参见 "adb help all")
adb shell - 交互运行远程 shell
adb shell <command> - 运行远程 shell 命令
adb emu <command> - 运行模拟器控制台命令
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - 查看设备日志
adb forward --list - 列出所有前向套接字连接。
格式是一个行列表,格式如下:
<serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
adb forward <local> <remote> - 前向套接字连接
转发规格是
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix 域名套接字名称>
localreserved:<unix 域名套接字名称>
localfilesystem:<unix 域名套接字名称>
dev:<字符设备名>
jdwp:<进程pid> (仅远程)
adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
- 与 "adb forward <local> <remote>" 相同,但如果 <local> 已经转发就会失败
adb forward --remove <local> - 移除特定的转发套接字连接
adb forward --remove-all - 移除所有前向套接字连接
adb jdwp - 列出托管 JDWP 传输的进程的 PID
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <文件>
- 将此软件包文件推送到设备并安装
('-l' 意味着对应用程序进行转发锁定)
('-r' 意味着重新安装应用程序,保留其数据)
('-s' 意味着安装在 SD 卡上,而不是内置存储器上)
('--algo', '--key', 和 '--iv' 表示文件已经加密)
adb uninstall [-k] <包名> - 从设备中删除此应用软件包
('-k' 是指保留数据和缓存目录)
adb bugreport - 返回错误报告中应包含的所有设备信息。
adb backup [-f <文件>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<包名...>]
- 将设备数据存档写入 <文件>。
如果没有提供 -f 选项,数据将写入当前目录下的 "backup.ab"。
(-apk|-noapk 启用/禁用存档中 .apk 本身的备份;默认为 noapk。)
(-obb|-noobb 启用/禁用与每个应用程序相关的任何已安装 apk 扩展(又名 .obb)文件的备份;
默认为 noobb。)
(-shared|-noshared 启用/禁用设备共享存储/SD 卡内容备份;默认为 noshared。)
(-all 表示备份所有已安装的应用程序)
(-system|-nosystem 切 换-all 是否自动包含系统应用程序;默认为包含系统应用程序)
(<包名...> 是要备份的应用程序列表。 如果传递了 -all 或 -shared 标志,
则软件包列表是可选的。 即使 -nosystem 通常会导致省略,
命令行中明确给出的应用程序也会包含在内。)
adb restore <file> - 从 <file> 备份存档恢复设备内容
adb help - 显示此帮助信息
adb version - 显示版本号
脚本:
adb wait-for-device - 阻止,直至设备联机
adb start-server - 确保有服务器在运行
adb kill-server - 如果服务器正在运行,则将其杀死
adb get-state - 打印:offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - 打印:<serial-number>
adb get-devpath - 打印:<device-path>
adb status-window - 连续打印指定设备的设备状态
adb remount - 重新挂载设备上的 /system 分区为读写
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - 重启设备,可选择进入引导加载程序或恢复程序
adb reboot-bootloader - 将设备重启至引导加载程序
adb root - 以 root 权限重启 adbd 守护进程
adb usb - 重启监听 USB 的 adbd 守护进程
adb tcpip <port> - 重启通过 TCP 在指定端口上监听的 adbd 守护进程
网络:
adb ppp <tty> [参数] - 通过 USB 运行 PPP。
注意:不应自动启动 PPP 连接。
<tty> 指 PPP 流的 tty。例如 dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[参数] - 例如 defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb 同步注意事项: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> 可以有多种解释:
- 如果未指定 <directory>,则 /system 和 /data 分区都将被更新。
- 如果是 "system" 或 "data",则只更新相应的分区。
环境变量:
ADB_TRACE - 打印调试信息。以逗号分隔的下列值列表
1 或 all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - 要连接的序列号。如果给定,-s 优先。
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - 与 logcat 选项一起使用时,只打印这些调试标记。adb 原始帮助文件
Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s <specific device> - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL
environment variable.
-p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or
a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
environment variable is used, which must
be an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push <local> <remote> - copy file/dir to device
adb pull <remote> [<local>] - copy file/dir from device
adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
(see 'adb help all')
adb shell - run remote shell interactively
adb shell <command> - run remote shell command
adb emu <command> - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
<serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
- same as 'adb forward <local> <remote>' but fails
if <local> is already forwarded
adb forward --remove <local> - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <file>
- push this package file to the device and install it
('-l' means forward-lock the app)
('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already)
adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb backup [-f <file>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<packages...>]
- write an archive of the device's data to <file>.
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
(<packages...> is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore <file> - restore device contents from the <file> backup archive
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number>
adb get-devpath - prints: <device-path>
adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
<tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> can be interpreted in several ways:
- If <directory> is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
environmental variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.Android Debug Bridge version 1.0.31
-a - directs adb to listen on all interfaces for a connection
-d - directs command to the only connected USB device
returns an error if more than one USB device is present.
-e - directs command to the only running emulator.
returns an error if more than one emulator is running.
-s <specific device> - directs command to the device or emulator with the given
serial number or qualifier. Overrides ANDROID_SERIAL
environment variable.
-p <product name or path> - simple product name like 'sooner', or
a relative/absolute path to a product
out directory like 'out/target/product/sooner'.
If -p is not specified, the ANDROID_PRODUCT_OUT
environment variable is used, which must
be an absolute path.
-H - Name of adb server host (default: localhost)
-P - Port of adb server (default: 5037)
devices [-l] - list all connected devices
('-l' will also list device qualifiers)
connect <host>[:<port>] - connect to a device via TCP/IP
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
disconnect [<host>[:<port>]] - disconnect from a TCP/IP device.
Port 5555 is used by default if no port number is specified.
Using this command with no additional arguments
will disconnect from all connected TCP/IP devices.
device commands:
adb push <local> <remote> - copy file/dir to device
adb pull <remote> [<local>] - copy file/dir from device
adb sync [ <directory> ] - copy host->device only if changed
(-l means list but don't copy)
(see 'adb help all')
adb shell - run remote shell interactively
adb shell <command> - run remote shell command
adb emu <command> - run emulator console command
adb logcat [ <filter-spec> ] - View device log
adb forward --list - list all forward socket connections.
the format is a list of lines with the following format:
<serial> " " <local> " " <remote> "\n"
adb forward <local> <remote> - forward socket connections
forward specs are one of:
tcp:<port>
localabstract:<unix domain socket name>
localreserved:<unix domain socket name>
localfilesystem:<unix domain socket name>
dev:<character device name>
jdwp:<process pid> (remote only)
adb forward --no-rebind <local> <remote>
- same as 'adb forward <local> <remote>' but fails
if <local> is already forwarded
adb forward --remove <local> - remove a specific forward socket connection
adb forward --remove-all - remove all forward socket connections
adb jdwp - list PIDs of processes hosting a JDWP transport
adb install [-l] [-r] [-s] [--algo <algorithm name> --key <hex-encoded key> --iv <hex-encoded iv>] <file>
- push this package file to the device and install it
('-l' means forward-lock the app)
('-r' means reinstall the app, keeping its data)
('-s' means install on SD card instead of internal storage)
('--algo', '--key', and '--iv' mean the file is encrypted already)
adb uninstall [-k] <package> - remove this app package from the device
('-k' means keep the data and cache directories)
adb bugreport - return all information from the device
that should be included in a bug report.
adb backup [-f <file>] [-apk|-noapk] [-obb|-noobb] [-shared|-noshared] [-all] [-system|-nosystem] [<packages...>]
- write an archive of the device's data to <file>.
If no -f option is supplied then the data is written
to "backup.ab" in the current directory.
(-apk|-noapk enable/disable backup of the .apks themselves
in the archive; the default is noapk.)
(-obb|-noobb enable/disable backup of any installed apk expansion
(aka .obb) files associated with each application; the default
is noobb.)
(-shared|-noshared enable/disable backup of the device's
shared storage / SD card contents; the default is noshared.)
(-all means to back up all installed applications)
(-system|-nosystem toggles whether -all automatically includes
system applications; the default is to include system apps)
(<packages...> is the list of applications to be backed up. If
the -all or -shared flags are passed, then the package
list is optional. Applications explicitly given on the
command line will be included even if -nosystem would
ordinarily cause them to be omitted.)
adb restore <file> - restore device contents from the <file> backup archive
adb help - show this help message
adb version - show version num
scripting:
adb wait-for-device - block until device is online
adb start-server - ensure that there is a server running
adb kill-server - kill the server if it is running
adb get-state - prints: offline | bootloader | device
adb get-serialno - prints: <serial-number>
adb get-devpath - prints: <device-path>
adb status-window - continuously print device status for a specified device
adb remount - remounts the /system partition on the device read-write
adb reboot [bootloader|recovery] - reboots the device, optionally into the bootloader or recovery program
adb reboot-bootloader - reboots the device into the bootloader
adb root - restarts the adbd daemon with root permissions
adb usb - restarts the adbd daemon listening on USB
adb tcpip <port> - restarts the adbd daemon listening on TCP on the specified port
networking:
adb ppp <tty> [parameters] - Run PPP over USB.
Note: you should not automatically start a PPP connection.
<tty> refers to the tty for PPP stream. Eg. dev:/dev/omap_csmi_tty1
[parameters] - Eg. defaultroute debug dump local notty usepeerdns
adb sync notes: adb sync [ <directory> ]
<localdir> can be interpreted in several ways:
- If <directory> is not specified, both /system and /data partitions will be updated.
- If it is "system" or "data", only the corresponding partition
is updated.
environmental variables:
ADB_TRACE - Print debug information. A comma separated list of the following values
1 or all, adb, sockets, packets, rwx, usb, sync, sysdeps, transport, jdwp
ANDROID_SERIAL - The serial number to connect to. -s takes priority over this if given.
ANDROID_LOG_TAGS - When used with the logcat option, only these debug tags are printed.fastboot 工具
fastboot 中文帮助文件
使用方法: fastboot [ <选项> ] <命令>
命令:
update <文件名> 从 update.zip 中重新刷新设备
flashall 刷入 boot + recovery + system
flash <分区> [ <文件名> ] 将文件写到闪存分区
erase <分区> 擦除一个闪存分区
format <分区> 格式化一个闪存分区
getvar <变量> 显示一个 bootloader 变量
boot <内核> [ <ramdisk> ] 下载并启动内核
flash:raw boot <kernel> [ <ramdisk> ] 创建 bootimage 并刷入
devices 列出所有连接的设备
continue 继续进行自动启动
reboot 正常重启设备
reboot-bootloader 重启设备进入 bootloader
help 显示此帮助信息
选项:
-w 擦除用户数据和缓存(如果分区类型支持,
则进行格式化)。
-u 格式化前不要先擦除分区
-s <特定设备> 指定设备序列号或设备端口的路径
-l 伴随 "devices",列出设备路径
-p <产品> 指定产品名称
-c <命令行> 覆盖内核命令行
-i <vendor id> 指定一个自定义的 USB 供应商 ID
-b <base_addr> 指定一个自定义的内核基址。 默认:0x10000000
-n <page size> 指定nand页的大小。 默认:2048
-S <size>[K|M|G] 自动疏散大于尺寸的文件。 0表示禁用使用方法: fastboot [ <选项> ] <命令>
命令:
update <文件名> 从 update.zip 中重新刷新设备
flashall 刷入 boot + recovery + system
flash <分区> [ <文件名> ] 将文件写到闪存分区
erase <分区> 擦除一个闪存分区
format <分区> 格式化一个闪存分区
getvar <变量> 显示一个 bootloader 变量
boot <内核> [ <ramdisk> ] 下载并启动内核
flash:raw boot <kernel> [ <ramdisk> ] 创建 bootimage 并刷入
devices 列出所有连接的设备
continue 继续进行自动启动
reboot 正常重启设备
reboot-bootloader 重启设备进入 bootloader
help 显示此帮助信息
选项:
-w 擦除用户数据和缓存(如果分区类型支持,
则进行格式化)。
-u 格式化前不要先擦除分区
-s <特定设备> 指定设备序列号或设备端口的路径
-l 伴随 "devices",列出设备路径
-p <产品> 指定产品名称
-c <命令行> 覆盖内核命令行
-i <vendor id> 指定一个自定义的 USB 供应商 ID
-b <base_addr> 指定一个自定义的内核基址。 默认:0x10000000
-n <page size> 指定nand页的大小。 默认:2048
-S <size>[K|M|G] 自动疏散大于尺寸的文件。 0表示禁用fastboot 原始帮助文件
usage: fastboot [ <option> ] <command>
commands:
update <filename> reflash device from update.zip
flashall flash boot + recovery + system
flash <partition> [ <filename> ] write a file to a flash partition
erase <partition> erase a flash partition
format <partition> format a flash partition
getvar <variable> display a bootloader variable
boot <kernel> [ <ramdisk> ] download and boot kernel
flash:raw boot <kernel> [ <ramdisk> ] create bootimage and flash it
devices list all connected devices
continue continue with autoboot
reboot reboot device normally
reboot-bootloader reboot device into bootloader
help show this help message
options:
-w erase userdata and cache (and format
if supported by partition type)
-u do not first erase partition before
formatting
-s <specific device> specify device serial number
or path to device port
-l with "devices", lists device paths
-p <product> specify product name
-c <cmdline> override kernel commandline
-i <vendor id> specify a custom USB vendor id
-b <base_addr> specify a custom kernel base address. default: 0x10000000
-n <page size> specify the nand page size. default: 2048
-S <size>[K|M|G] automatically sparse files greater than
size. 0 to disableusage: fastboot [ <option> ] <command>
commands:
update <filename> reflash device from update.zip
flashall flash boot + recovery + system
flash <partition> [ <filename> ] write a file to a flash partition
erase <partition> erase a flash partition
format <partition> format a flash partition
getvar <variable> display a bootloader variable
boot <kernel> [ <ramdisk> ] download and boot kernel
flash:raw boot <kernel> [ <ramdisk> ] create bootimage and flash it
devices list all connected devices
continue continue with autoboot
reboot reboot device normally
reboot-bootloader reboot device into bootloader
help show this help message
options:
-w erase userdata and cache (and format
if supported by partition type)
-u do not first erase partition before
formatting
-s <specific device> specify device serial number
or path to device port
-l with "devices", lists device paths
-p <product> specify product name
-c <cmdline> override kernel commandline
-i <vendor id> specify a custom USB vendor id
-b <base_addr> specify a custom kernel base address. default: 0x10000000
-n <page size> specify the nand page size. default: 2048
-S <size>[K|M|G] automatically sparse files greater than
size. 0 to disable版权声明
本文档已获得 @灬只会刷机养老 授权搬运并修改整理
相关链接
- 常见问题与解答 > 文档说明:命令的使用
- 基础知识 > 名词集:命令与终端
- Android 调试桥 (adb) - Android 开发者
- Android 调试桥 (adb) (新版) 英文 - Android 开发者
- SDK 平台工具版本说明 - Android 开发者
参考链接
- ADB - 百度百科
- Android 调试桥 (adb) - Android 开发者
- SDK 平台工具版本说明 - Android 开发者
- 【小白搞机入门】第四期-配置adb环境和fastboot环境(Android SDK) - 酷安:@灬只会刷机养老